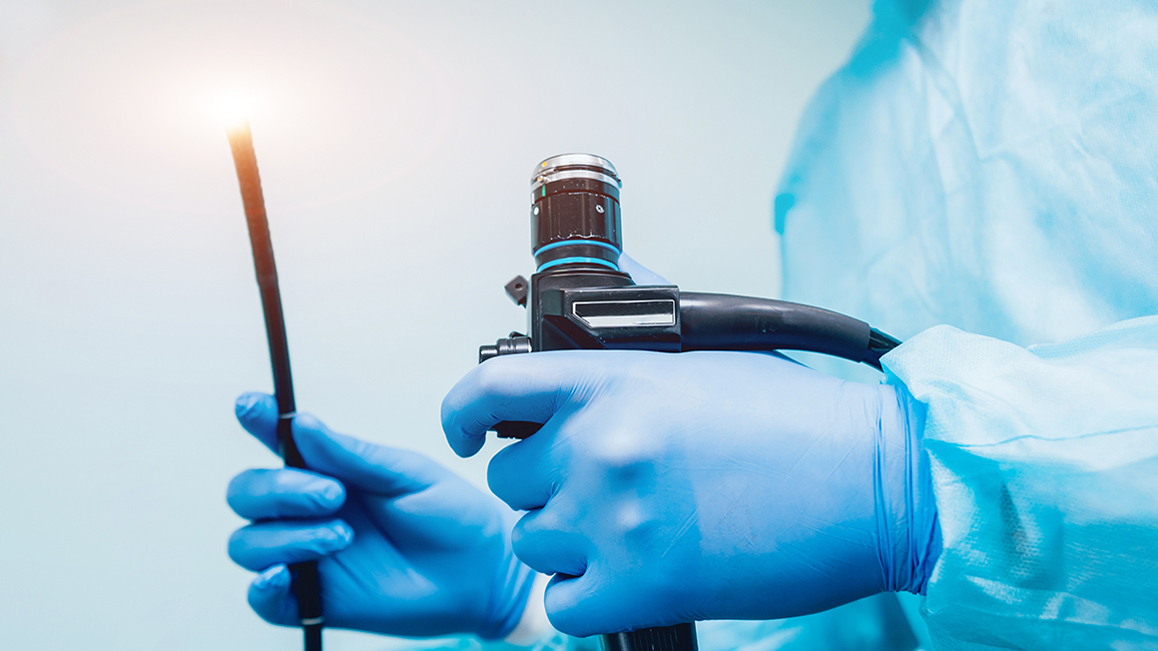
Endoscopy is a procedure used to diagnose diseases of the upper GI tract, particularly the esophagus, the stomach, and the duodenum. The procedure is sometimes combined with an ultra sound and helps diagnose digestive disorders, nausea, abdominal pain and cramping, celiac disease, gastritis etc. The upper endoscopy is a non-surgical procedure and lasts between 15 to 30 minutes. The patient will be administered a numbing spray to prevent gagging and may also ask for sedation if required. A thin flexible tube fitted with a camera is passed through the mouth and throat into the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the small intestine. The doctor views the pictures on a monitor and may collect samples of any ulcers present. Doctors may sometimes recommend an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, a form of endoscopy that also allows visual images of the pancreas, gall bladder, etc.